Toolbox for Individualized and Evidence-Based Nutritional Management
Clinicalnutrition.science is an independent website designed to facilitate individualized and evidence-based nutritional management for patients. The algorithms and data are based on the results of large clinical studies such as the EFFORT study, allowing the transfer of knowledge from theory to practice.
Overview of All Tools

NutriScreen
A selection of commonly used, recognized, and validated screening and diagnostic tools for identifying patients with manifest malnutrition or an increased risk of malnutrition.

NutriCalc
A selection of established formulas for the individual calculation of energy and protein requirements, providing a basis for additional nutritional therapy.

NutriGo
Application-oriented and practical recommendations for nutritional therapy in various disease situations, with the option to calculate individual nutritional goals based on current guidelines.

NutriPro
Comprehensive product database containing all available nutritional drinks, enteral and parenteral nutrition products, and related information.

NutriPlate
The digitized plate model is a simple and visual tool for nutritional counseling. It illustrates to patients how to optimally compose their main meal (breakfast, lunch, or dinner).
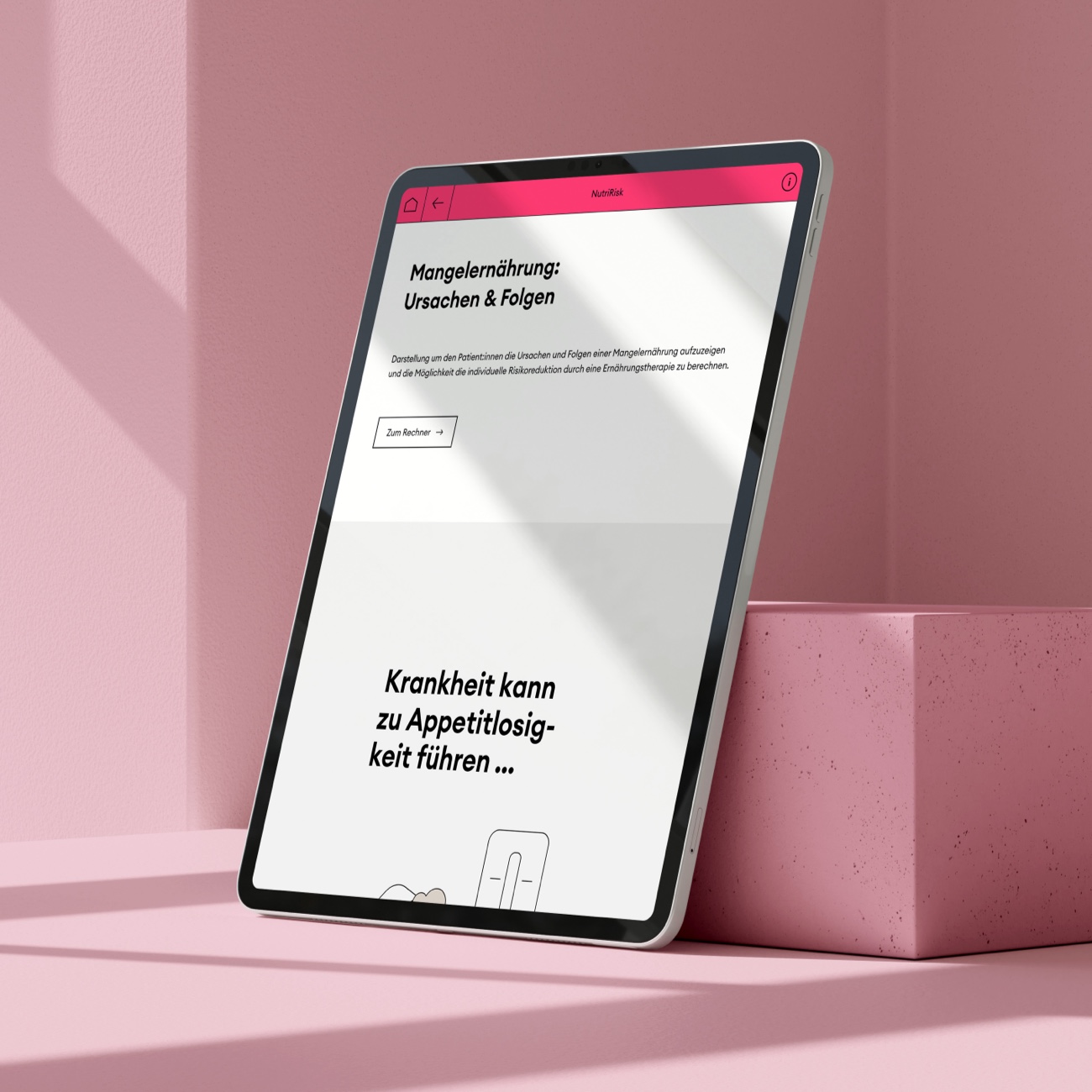
NutriRisk
Scroll animation to show patients the causes and consequences of malnutrition and the possibility of calculating the individual risk reduction through nutritional therapy.

NutriBib
A reference work for leading, current, and selected literature in the field of clinical nutrition, with abstracts and links to original publications.
Questions & Contact
For questions about this website, please contact us.